Charging Your Car
Generally, you will charge your car at home, or when commuting, on a work charger or if travelling on a public charger. Your home charger can deliver a max of 7.4kW AC (Alternating Current) power. Most cars will come with an AC portable charging cable.
Home Charger

There is a wide choice of EV chargers available on the market. Some car manufacturers will recommend a preferred supplier while others will leave it up to the customer to choose their own.
The Electric Vehicle Home Charger Grant provides a grant up to the value of €300 towards the purchase and installation of a home charger unit for residents and homeowners on their property.
To receive payment, you must ensure that you use a Safe Electric Registered Electrical Contractor, installation usually takes around 3 hours, and you must ensure you receive approval before commencing any works. The installer will arrange a survey and assist you in selecting a charger. The grant is open to homeowners to apply for a grant, whether they own an electric vehicle or not.
The SEAI who administers applications, maintains a list of chargers that meet specific criteria. Home EV chargers are wall-mounted to the property and with a tethered charging lead the process of charging is easy, convenient, and a cheaper way to charge. Visit SEAI.ie
Public Chargers
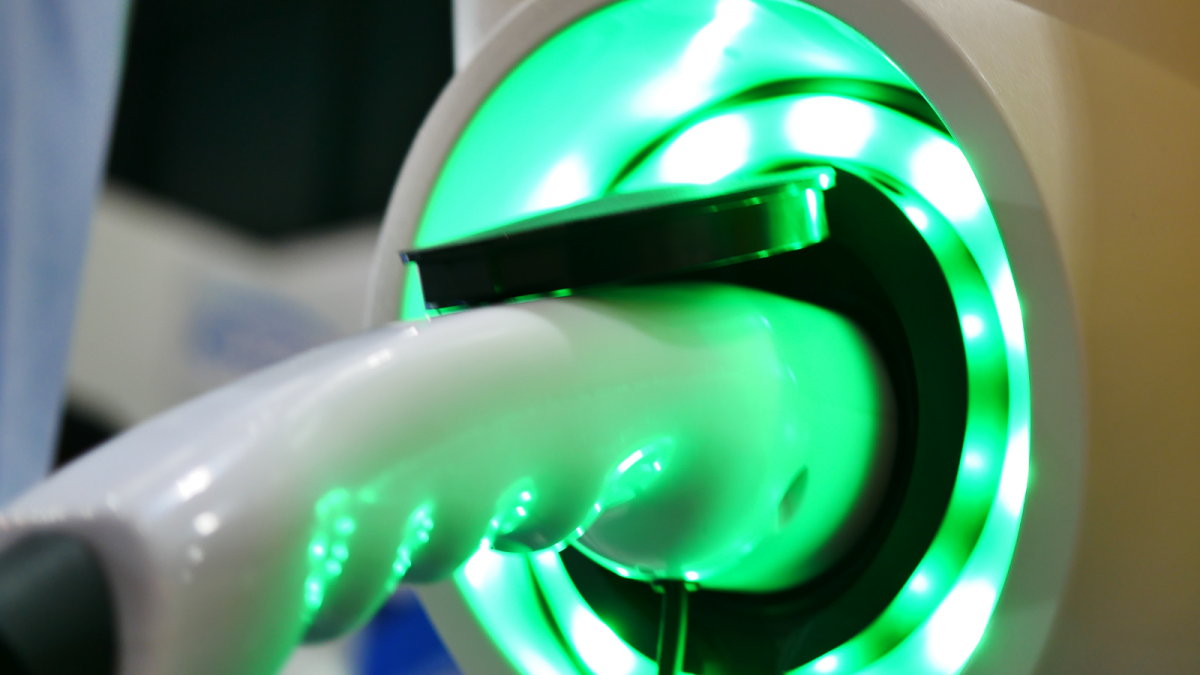

On the public charging network, there are generally 3 different types of chargers.
1. Standard charger- (up to 22Kw AC) can charge your car in approximately 1-6 hours.
2. Fast Charger- (up to 50Kw DC) can charge a car up to 80% in as little as 30 minutes.
3. High Power Charger- (from 50kW to 350kW DC) can provide up to 100km of driving range in as little as six minutes.
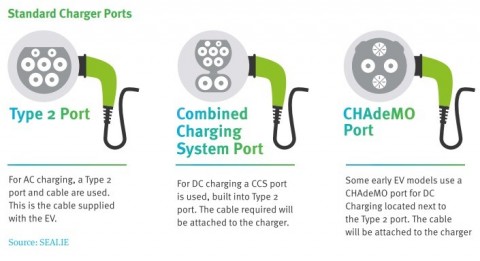
Charger Ports
– Ensure you know where the charging ports are, how to open them and which is AC/DC.
– There is an AC charging cable in the car.
Public Charging Network
Charging an electric vehicle can be done through the National Charging Infrastructure which operates throughout the island of Ireland (both fast and slow charging). To locate public charging stations for topping up while out and about, visit the ESB Ecars interactive map to find the nearest ESB charge point to you. ESB owns, operates, and maintains approximately 1,600 public charge points across Ireland.
You register online, where you will see details of charging costs, set up an account, receive a charge point access card or fob, and download their app to locate your nearest charger. There are many other charging operators in the market also and the charge point will usually display details of how you can sign up for their service. The network of EV charging stations continues to expand.
Cost of Charging
For many EV owners, their charging will be done at home as the cost will be significantly less than charging using public charge points. Homeowners have the advantage of monitoring and charging at slower rates which is usually more cost-effective, and they can avail of a cheaper overnight rate when charging. Charges between domestic suppliers will vary, so homeowners should consult their energy provider.
Public charger providers generally will offer a pay-as-you-go or pre-pay subscription service. There is usually an overstay fee for charging sessions longer than 45 minutes and after ten hours on standard chargers. General recommendations are to charge to around 80%, as the charging speed will slow down significantly to charge the final 20%. Charging costs are subjective, as the cost to charge will depend on your car’s battery size (which varies between car models), for example a larger battery will take longer to charge, the unit price of electricity, and the method of charging. However, the cost of charging is cheaper than a petrol or diesel car. For public charging costs, consult the providers website, as they will display the cost per kWh.